Cells appear in a confounding show of grounds and shave. Some move quickly and have quick creating structures, as should be clear in motion pictures of amoebae and rotifers. Others are commonly fixed and on an extremely fundamental level steady. Oxygen slaughters two or three cells yet is a totally basic for other people.
Most cells in multicellular creatures are eventually related with different cells. In spite of the fact that some unicellular living animals live in disconnection, others structure states or live in comfortable relationship with different sorts of living things, for example, the living beings that help plants to detach nitrogen from the air or the microorganisms that live in our stomach related organs and help us with getting ready food.
Despite these and distinctive assorted disparts, all phones share certain associate highlights and do many tangled methods in on an exceptionally essential level a relative way. As the record of cells spreads out all through this book, we will concentrate on the atomic explanation of both the capabilities and similitudes in the structure and cutoff of different cells.
All Cells Are Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic.
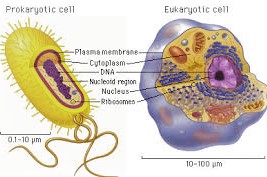
The ordinary universe incorporates two sorts of cells—prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells incorporate an offense single shut compartment that is hovered by the plasma film, doesn’t have a portrayed focus, and has an unobtrusively central inside alliance. All prokaryotes have cells of this sort.
Living beings, the most various prokaryotes, are single-celled living animals; the cyanobacteria, or blue green turn of events, can be unicellular or filamentous chains of cells. However bacterial cells don’t have layer compelled compartments, different proteins are precisely kept in their fluid inside, or cytosol, showing the nearness of inward connection.
A particular Escherichia coli bacterium has a dry stack of about 25⨯ 10⨯14 g. Microorganisms address a typical 1–1.5 kg of the standard human’s weight. The assessed number of little living things on earth is 5 ⨯ 1030, estimating an aggregate of around 1012 kg. Prokaryotic cells have been discovered 7 miles some spot down in the sea and 40 miles open to address; they are outstandingly versatile! The carbon put aside in microorganisms is close as much as the carbon put aside in plants.
Eukaryotic cells, instead of prokaryotic cells, contain a depicted layer bound focus and far reaching inside membranes that encase different compartments, the organelles. The territory of the cell lying between the plasma film and the middle is the cytoplasm, including the cytosol (watery stage) and the organelles. Eukaryotes contain all individuals from the plant and creature spaces, including the parasites, which exist in both multicellular structures (molds) and unicellular structures (yeasts), and the protozoans (proto, grungy; zoan, creature), which are solely unicellular.
Eukaryotic cells are generally around 10–100 ⨯ m over, for the most part fundamentally more noteworthy than living beings. A normal human fibroblast, a connective tissue cell, may connect with 15 ⨯ m across with a volume and dry weight some spot in the extent of thousands of times those of an E. coli bacterial cell. A one-celled critter, a solitary celled protozoan, can be more than 0.5 mm long. An ostrich egg starts as a solitary cell that is astonishingly more noteworthy and effectively obvious to the free eye.
http://feeds.feedburner.com/ecarepk