Blunt and Sticky ends:
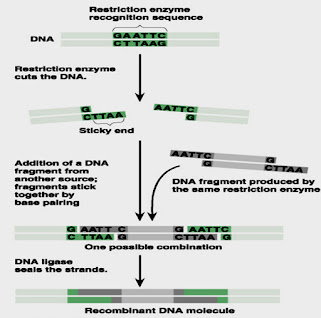
- The ends that we called sticky ends or also called cohesive ends these have longer overhangs of nucleotides sequences at the one end.
- These longer overhangs are the stretches of unpaired nucleotides sequence.
DNA ligases:
- These are the DNA fragments joining enzymes.
- DNA ligase enzymes obtained from E. coli and from phage T4.
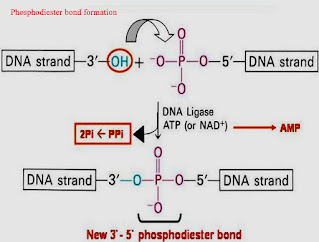
- Its function is to seal different single strands nick between the adjacent molecule in the duplex
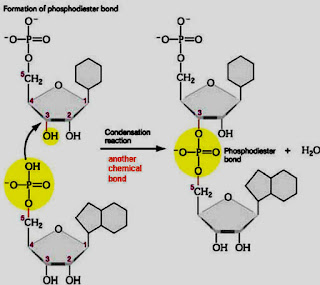
- This happened by the formation of the covalent bond which is phosphodiester bond between the acceptor 3′ hydroxy end and donor 5′ phosphoryl in a double stranded DNA molecule.
- Ligation reaction is one which is dependent on ATP adenylation which is the addition of AMP pf the 5′ phosphate formation of pyrophosphate bond take place and than it will react with the 3′-hydroxy and creates a phosphodiester bond.
- Ligase enzyme that is obtained from the E. Coli required NADP for performing ligation reaction.
- And ligase enzyme that obtained from T4 phage require ATP.
- When vector and gene of interest is cut down by the restriction enzymes into the sticky end than here is the work of the ligases is to bind nick between the gene of interest and vector and it will form a recombinant vector.
- But the problem lies for the blunt ends that are difficult to join.
- Self ligation of the vectors can also happened at the higher rate rather than recombination of vector and gene of interest.
The problems of blunt ends are overcome by using following methods:
- Use of linkers.
- Use of adaptors
- Use of homopolymer tail.
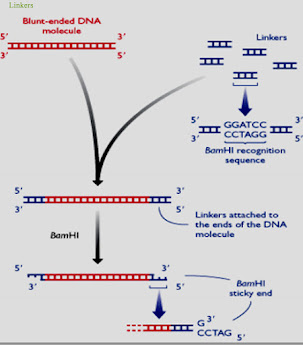
linkers:
- These linkers are commonly used to link blunt ends of the gene of interest with the vectors having sticky ends.
- These linkers are actually normally synthesized which are self-complementary oligonucleotides than endonucleases recognize these sites as linkers have recognition sites and it creates sticky ends.
- First of all linkers are attached or ligated at both blunt ends of gene of interest and than cut down by the endonucleases which are restriction enzymes in order to generate sticky ends.
- Than now this gene of interest that have sticky ends can easily be inserted into the vector which is also cleaved by the same restriction enzyme and now have sticky ends.
- Than at the end insertion that is take place by the linker it creates restriction enzyme recognition site at the both ends of the foreign gene and than it makes the this foreign gene able to excised and recovery take place after cloning amplification take place in the host bacteria.
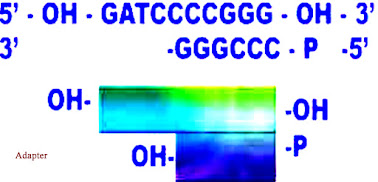
Adapters:
- It happened as multiple linkers can attach with the blunt end of the gene of interest.
- It will make larger gene having a lot of linkers attach thus this is the wastage of the linkers.
- To deal with this problem adapters are used.
- Adapters have only one end that is suitable for joining.
- Thus this makes possible the joining of less adapters preventing from over length and wastage of the adapters.
- Adapters are used to attach sticky ends with the blunt ends and these are actually synthetic , double stranded oligonucleotides.
- Adapters actually lack 5’end phosphate group on the sticky end this will prevent the polymerization of the adapters.
- When the attachment of the adapter have done than the unnatural 5′-OH end was converted in to the functional or natural 5’phosphate group this happened by he treatment with the polynucleotide kinase enzyme which will generate sticky end that fragment having sticky end now easily can be inserted into the vector.
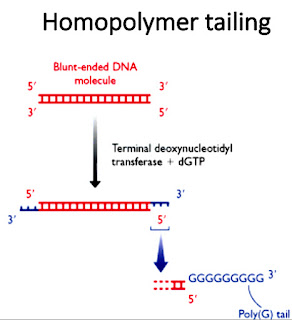
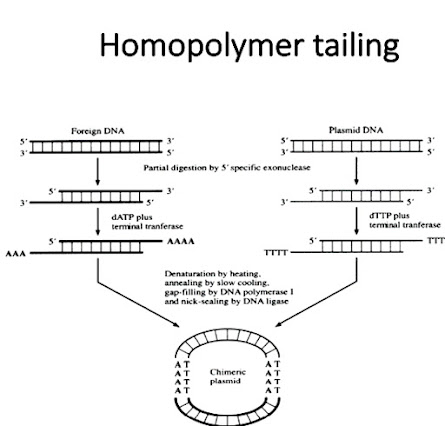
Homopolymer tailing:
- A homopolymer is a polymer made up of the same sub-units.
- This homopolymer tailing method involves the use of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase enzyme that adds the series of the same nucleotide at he 3′-OH terminal of the double stranded DNA molecule.
- If the same deoxynucleotide is added in this process than homopolymer tailing is produced.
- In homopolymer tailing the blunt end of the gene of interest is tailed with on kind of series of nucleotide while the end of the vector is tailed with the complementary base.
- Than the vector is recombined with the only gene of interest and here self ligation is mostly prevented because of lack complementary ends
http://feeds.feedburner.com/ecarepk