Definition
The vitality changes in organic frameworks is called Bioenergetics. Vitality can be characterized as the capacity to accomplish work. Bioenergetics predominantly manages the vitality changes in the living creatures.
Laws of Thermodynamics
The vitality is the contribution to a cycle where as the yield is the work. The fundamental standards of thermodynamics structure the rudiments of the bioenergetics.
1, The Law of protection of Energy
The principal law of the thermodynamics expresses that the all out vitality substance of the universe is steady. Vitality can nor be made nor crushed. In any case, one type of vitality can be changed over into another structure.
2 Spontaneous process
The second law of thermodynamics expresses that occasions move from a higher vitality level to bring down vitality level unexpectedly and arrive at balance. Responses continue toward a path with increment in entropy( Entropy is a proportion of scattering and arbitrary developments) and reduction in Free vitality.
Bioenergetics
The living frameworks are equipped for driving numerous non-unconstrained responses, which require vitality for combination and exceptionally requested structures. Staple and brilliant vitality are utilized for such non-unconstrained responses. While building such exceptionally requested structures a net decline in entropy happens in Living frameworks.
Kinds of Biological responses
There are two kinds of concoction responses that happen in our body .
1. Exergonic responses in the living framework the exergonic responses free vitality to perform work. It is an unconstrained response. Eg. ATP Hydrolysis
2. Endergonic response: In the living framework the Endergonic responses gets vitality from outside to play out a work. It is a non-unconstrained response. Eg. Food and brilliant energy.3. Living frameworks are far away from the balance. At the point when it arrives at the condition of harmony the passing of living framework happens.
4. Study state (Net change is zero) is a reasonable condition of unconstrained cycle and non-unconstrained cycle. Eg. Separating of sugars or proteins.
Instances of Bioenergetics
1. Chloroplast Bioenergetics
During photosynthesis to create one atom of glucose 48 photons are utilized. One particle of glucose stores 686 K cal of substance vitality. Complete contribution of vitality of 48 particles of photons is 48X 42 K cal. The effectiveness of generally speaking cycle can be determined as follows.
Productivity: OUTPUT/INPUT X 100 = 686/48 X 42 X100= 34.02 %
2. Mitochondrial Bioenergetics
Oxidative phosphorylation happens in Mitochondria. The measure of vitality put away per particle of ATP is 8 K cal. The measure of free vitality put away in 3 moles of ATP is 3 X 8 = 24 K cal.
Vitality delivered by one mole of NADH oxidation is 53 K cal. Productivity: OUTPUT/INPUT X 100 = 24/8 X 3 X100= 45.28 %
The Nature of ATP
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the vitality cash or coin of the cell that moves vitality from concoction bonds to Endergonic(energy retaining) responses inside the cell. Fundamentally, ATP comprises of the adenine nucleotide (ribose sugar, adenine base, and phosphate gathering, PO4 – 2) in addition to two other phosphate gatherings.
1) Substrate-level phosphorylation;
2) Chemiosmosis
1. Substrate-level phosphorylation
Happens in the cytoplasm when a protein appends a third phosphate to the ADP (both ADP and the phosphates are the substrates on which the chemical demonstrations). This is outlined underneath.
2. Chemiosmosis
During Chemiosmosis in eukaryotes, H+ particles are siphoned over an organelle layer by film “siphon proteins” into a limited space (limited by layers) that contains various hydrogen particles. The vitality for the siphoning originates from the coupled oxidation-decrease responses in the electron transport chain. Electrons are passed from one layer bound protein to another, losing some vitality with each move (according to the second law of thermodynamics).
This “lost” vitality takes into consideration the siphoning of hydrogen particles against the focus angle (there are less hydrogen particles outside the limited space than there are inside the restricted space).
The restricted hydrogens can’t go back through the layer. Their lone exit is through the ATP integrating catalyst that is situated in the restricting layer. As the hydrogen goes through the ATP incorporating chemical, vitality from the compound is utilized to connect a third phosphate to ADP, changing over it to ATP.
Generally the terminal phosphate isn’t just taken out, yet rather is joined to another particle. This cycle is known as phosphorylation.
BIOENERGETICS
1. When ATP discharges vitality, the response discharge just includes breaking the remainder of three phosphate bonds in the particle. This outcomes in the creation of a little controlled measure of vitality that is the perfect sum for the greater part of the vitality utilizing expending cycle of the cell.
2. Energy delivery since it includes breaking only the one phosphate bond implies that ATP can without much of a stretch be assembled by taking ADP and adding phosphate to it. Accordingly the results of vitality discharge from ATP can be reused by the cell to make new ATP. In the event that such a cycling among ADP+Phosphate and ATP were impractical our bodies would require gigantic measures of ATP. To perceive what I mean inspect the table beneath for ATP prerequisites for a “straightforward” microbes cell
The ATP Cycle.
1. Lipman hypothesized the ATP cycle
2. ATP is framed from ADP and Pi by photosynthesis in plants and by the digestion of vitality rich mixes in many cells.
3. The hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and Pi is connected to many key cell works; the free vitality delivered by the breaking of the phosphor an hydride bond is caught as usable vitality
4. Cellular breath makes ATP by joining phosphate gatherings to ADP to make the ATP
5. The cell utilizes the ATP to accomplish work. As a major aspect of this cycle the substance connection between the third phosphates bunch in the ATP is broken and vitality is moved to different atoms of the cell and lost as warmth.
6. ADP and phosphate created by the breakdown are currently reused into cell breath.
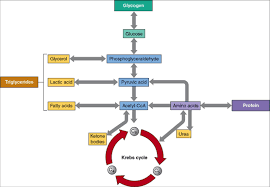
ATP doesn’t do anything in the Krebs cycle; it is the result of the cycle. Presently, glycolysis goes before the Krebs cycle, and it requires a venture of 2 particles of ATP to deliver 4. Glycolysis separates glucose into 2 3-carbon atoms of pyruvate.
The pyruvate moves into the mitochondria, where it enters the Krebs cycle, and is additionally separated (in a few stages) to carbon dioxide and water. The motivation behind these means is (through the electron trans ATP is framed from ADP and Pi by photosynthesis in plants and by the digestion of vitality rich mixes in many cells.
The hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and Pi is connected to many key cell works; the free vitality delivered by the breaking of the phosphoanhydride bond is caught as usable vitality.