The way toward parting a hereditarily homogeneous populace into at least two populaces that experience hereditary separation and inevitable conceptive detachment is called speciation.
Allopatric Speciation.
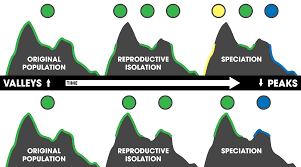
Allopatric speciation or geographic speciation will be speciation that happens when natural populaces of similar species become secluded because of geological changes, for example, mountain building or social changes, for example, displacement.
The disengaged populaces at that point experience genotypic as well as phenotypic disparity as: (a) they become exposed to various particular weights, (b) they freely experience hereditary float, and (c) various changes emerge in the populaces’ genetic supplies.
The different populaces after some time may develop particularly various attributes. On the off chance that the topographical hindrances are later evacuated, individuals from the two populaces might be not able to effectively mate with one another, so, all things considered, the hereditarily segregated gatherings have risen as various species.
Allopatric segregation is a key factor in speciation and a typical procedure by which new species emerge. Versatile radiation, as saw by Charles Darwin in Galapagos finches, is an outcome of allopatric speciation among island populaces.
Disconnecting Mechanisms.
Topographical disengagement: Geological procedures can part a populace through such occasions as development of mountain ranges, gorge arrangement, frigid procedures, the arrangement or decimation of land spans, or the subsidence of huge waterways. On a worldwide scale, plate tectonics are major land factors prompting partition of populaces and the subsequent conveyance of species.
The degree to which a geographical hindrance can adequately segregate a populace connects to the portability of the life form or its posterity. For instance physical hindrances, for example, gorge may adequately square movement and dispersal of little warm blooded animals; notwithstanding, have little effect on flying feathered creatures or wind-borne seeds.
Populace Dispersal: Population dispersal is utilized to depict transitory occasions, either as range extension (regular development away from guardians) or hop dispersal (intersection of obstructions), which may prompt hereditary confinement.
On the off chance that the littler populace part turns out to be hereditarily separated from the parental gathering, it might be exposed to its own interesting transformations, determination powers, and hereditary float impacts; along these lines, it will follow its own developmental pathway.
Movements or coincidental migrations, (for example, winged animals being brushed off kilter) may prompt populace parts; whereby bunches just become isolated by separation. When quality stream between the two gatherings is upset, speciation turns into a chance.
Allopatric speciation in fringe populaces.
At the point when populaces become hereditarily disconnected, heritable varieties may amass with the goal that they become not the same as the parental populace. Given adequate time, these varieties may prompt conceptive detachment.
Segments of a populace that exist along the edges of the parent populace’s geographic region have higher probability of creating regenerative seclusion. Such fringe populaces are probably going to have qualities that are not the same as the parental populace. After disconnection, the establishing populace is more averse to speak to the genetic stock of the parent populace.
What’s more, fringe disconnects are probably going to speak to few people, which means their genetic supply is progressively defenseless with the impacts of hereditary float (irregular possibility). Moreover, all things considered, the fringe populace will possess a domain not the same as its hereditary genetic stock, likely making it be exposed to various specific weights as it colonizes new regions.
The external fringe of a populace’s territory will in general be outrageous; consequently, the explanation go development is held under control. For most fringe secludes, all things considered, they cease to exist instead of endure and speciate.
Beginning of conceptive boundaries.
Versatile dissimilarity may happen when a populace turns out to be geologically separated: trailed by a gathering of hereditary contrasts as they adjust to their own one of a kind situations. Conceptive boundaries don’t advance as an outcome of outside powers that drive populaces toward speciation.
Or maybe, the advancement of conceptive disconnection, prompting speciation, is for the most part thought to be an accidental result of hereditary disparity, especially versatile changes that develop through regular determination in light of various ecological conditions in isolated geographic zones.
Sympatric speciation.
Sympatric speciation is the procedure through which new species advance from a solitary tribal animal types while possessing the equivalent geographic locale. In transformative science and biogeography, sympatric and sympatry are terms alluding to life forms whose reaches cover or are even indistinguishable, with the goal that they happen together at any rate in certain spots. On the off chance that these living beings are firmly related (for example sister species), such a circulation might be the consequence of sympatric speciation.
http://feeds.feedburner.com/ecarepk