According to the UN convention on biological Diversity the definition of microbial biotechnology can be define as:
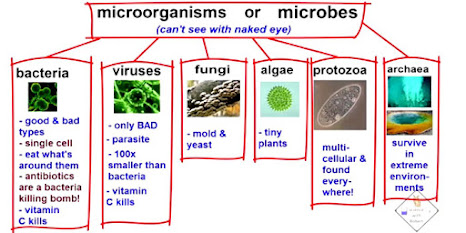
Microbial diversity:
- microbial biotechnology works by increasing the potential of micro-organisms to make them able work for the benefit of mankind.
- micro-biotechnology is proved to be the oldest form of biotechnology like people from centuries involved in making breads and curd by using micro-organism.
- application of fermentation that are used in the manufacturing of the wine and beverage is the same commonly used technology
- today in this era of science micro-organism are more extensively used in different form in different fields.
- the micro-organism that are used in this technology can be mutants, naturally isolates, laboratory cultured or can be genetically engineered that are synthesized using recombinant technology.
- the production of antibiotics using the technique of fermentation was the biotechnological breakthrough that was after world war II. So here below are the some major products of microbial biotechnology.
- penicillium:
obtained from penicillium chrysogenum
- Streptomycin:
- insulin, growth hormones and interferons:
obtained from E. Coli by the recombinant technology
- hepatitis B surface antigen:
- secondary metabolites that are not essential for the growth of the cell and proper functions these are actually synthesized in the later stage of the growth cycle. Antibiotics are also metabolites having anti bacterial activity.
- Microbial enzymes are also used in the laboratory extensively. like:
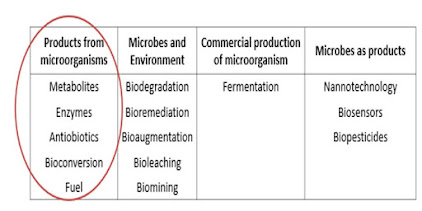
- advantage of the microbial products over the chemical synthesized products
Bio- processing:
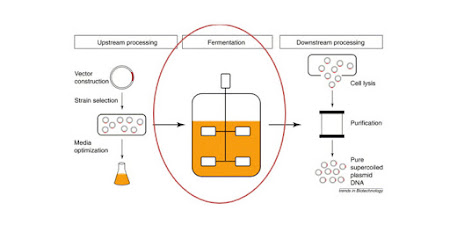
Fermentation:
- it is either aerobic or anaerobic process that utilizes mass culture of micro-organisms.
- any biological process that can take place in the absence of oxygen.
- it can be called food spoilage.
- it is also know as the production of the alcoholic beverage.
- it is the basic technique used in the microbial biotechnology lab in industry level.
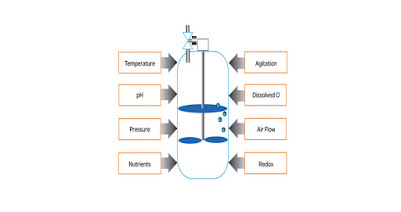
- like other chemical reaction the microbial growth is also the function of physical, chemical and nutritional conditions.
- when the condition are suitable the micro-organism will extract nutrients from the medium and covert them into useful chemical products.
Characteristics of fermentation:
- microbial nutrient culture:
micro-organism require nutrients like carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, phosphorus, sulfur and nitrogen for proper growth.
- Sterilization of the culture media:
- Environment for microbial growth:
- temperature: so low temperature can reduce growth, optimum temperature cause optimum growth and than the high temperature cause microbial death.
- pH
- Aeration and mixing
Fermentation at industrial level:
- on industrial scale fermentation performed in the large tanks that are called fermenter or bioreactor.
- two methods of fermentation used in the industrial scale:
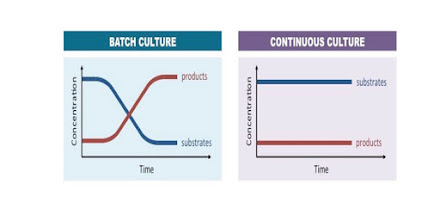
- Batch fermentation
- Continuous fermentation
Fermentation at industrial level:
Food Biotechnology:
- it is define as any technique that involve modification and manipulation of the genes of the animals, plants or other micro-organisms in order to either enhance market r production of the nutrients related products and their properties.
- fermentation is either oldest but till now a classical method used in the food biotechnology. cheese was the first biotechnology product that was synthesized by the nomadic tribes in Asia. today this technique is most commonly used in the dairy and beverage industry.
- now the modern food biotechnology depends on the recombinant DNA technology. Flavr Savr was the first food product that was derived using this modern technology.
- Golden rice is one of the other food product derived using this modern technology. it contain high content of beta-carotene it is especially derived to combat with the vitamin A deficiency related disease .
- now such derived products are called genetically modified products.