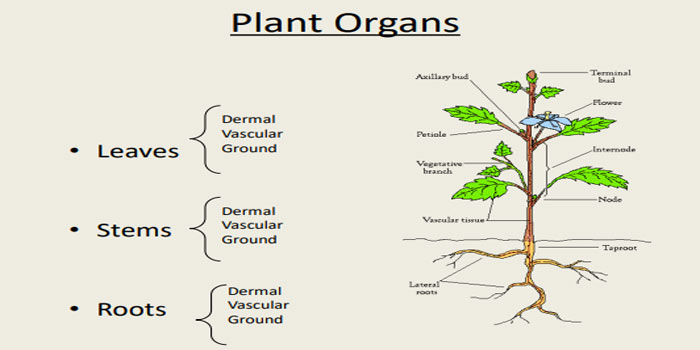
Function of the organs of the plants:
- Roots performs the function of anchorage, roots absorb water and other nutrients from the soil, transport of the nutrients and water and the function of storage.
- Stem provides the function of the support to the complete plant body and moreover the transport of the nutrients and the water.
- photosynthesis which is the production of the food is performed by the leaves.
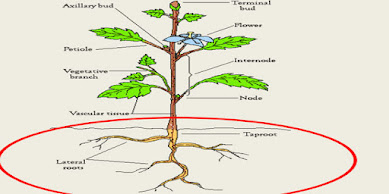
Roots:
- Roots which also called the hidden half of the plant
Function performed by roots:
- it include Anchorage of the plant body.
- it perform absorption of water and the other dissolved minerals.
- storage of the surplus sugar and the starch is done by the roots.
- roots attracts beneficial micro-organisms and different fungi that can improve plant growth.
- roots conducts water and nutrients to the entire plants
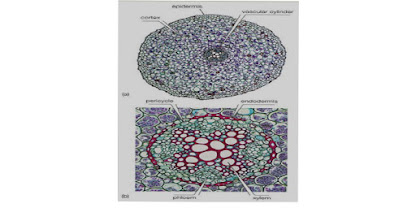
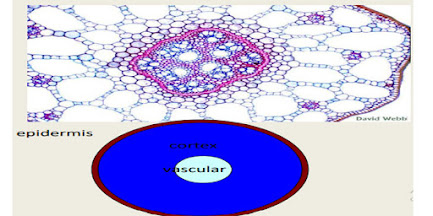
Anatomy of roots:
Tissue of the roots:
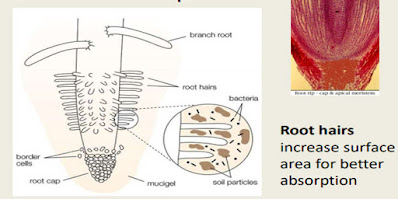
- Roots epidermis: it is the outer most layer of the cells, that is to protect plant from the different diseases . its function includes absorption of nutrients and water.
- tubular extension of the epidermal cells that is called root hair.
- the function of the root hair is to increase the surface area of the roots to increase the absorption of the nutrients and water
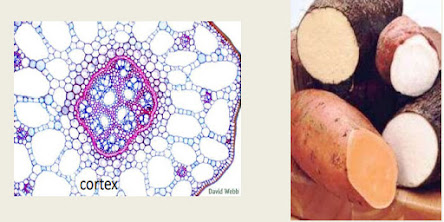
Root ground Tissues:
- Cortex are the ground tissues in case of the roots.
- the function of the ground tissues (which is root cortex) is to provide support and to store food like starch and sugar.
- its example is sweet potato where food is stored in the root cortex.
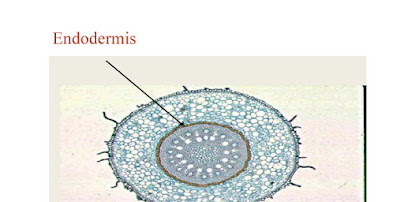
Root cortex : endodermis layer of the cells.
- cortex’s inner most layer which is actually called endodermis.
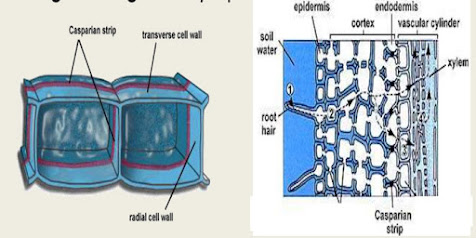
Root cortex: Casparian strip
- Casparin strips are present in the endodermis which is the inner layer of the cortex it is the water-impermeable strip which is made up of waxy material.
- Casparin strips create a barrier to have a control over uptake of materials into the xylem.so that material have to move through the cytoplasm of the cell.
http://feeds.feedburner.com/ecarepk