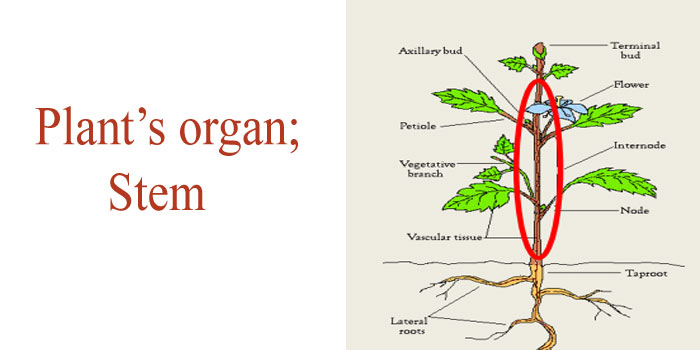
Stem:
- Stem is the organ of the plant that is above ground.
- its function is to support fruits and the leaves.
- through xylem and phloem it conduct water to the whole plant.
Stem’s Anatomy:
- stem internal structure shows it has dermal tissues , vascular tissues and the ground tissues.
Types of the Stem:
- there are the two types of the stem like herbaceous stem and the second one is the Woody stem.
Tissues of the Stem:
- outermost layer that is made up of dermal tissues like epidermis cells.
- it provides protection to the plant body.
- stem’s epidermis has waxy cuticle, that’s function is to prevent from water loss.
- stem on their epidermis has hair like trichome that is used for protection and than releases scant and oil etc.
Stem vascular tissues:
- in stem vascular tissues is composed of xylem and phloem.
- here xylem is used for the conduction of water.
- while phloem is used for the conduction of food and provides support to the plant.
Vascular Cambium:
- vascular cambium is basically present in the woody stem.
- vascular cambium is basically present between xylem and phloem mean among vascular bundle.
Vascular tissue in case of trees:
in case of tree vascular tissue located on the outer most layer of the tree.
Formation of ring by the vascular tissue in the trees:
http://feeds.feedburner.com/ecarepk