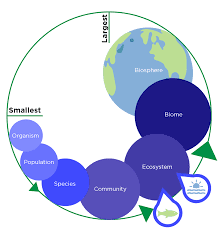
Apparently only earth harbours life one of the most fundamental attributes of life is that living life forms continuously interface with their condition and can not consider the decent variety of life on earth without understanding anything about a few biological laws that actually affect them, even on earth, life is contained inside a slight façade near the surfing planet.
Biosphere
however in this range, every sort of creature has built up an alternate arrangement of resistances for an assortment of ecological conditions eg.
Temperature of fluid water
Most creatures are adjusted to temperatures between 68-104ºF (20º-40ºC) life requires fluid water all life is made generally of water eg. people 60-70 % life is fundamentally a progression of substance responses
Metabolism
What’s more, you can’t have substance responses except if the synthetic concoctions are broken up in fluid no water no digestion nonetheless, a few creatures can briefly stop digestion when there is no water yet still endure eg. tardigrades, nematodes solidified water is equivalent to no water by any stretch of the imagination there can be no digestion likewise freezing slaughters since sharp ice gems grow and tear the cells open
However a few creatures can get by underneath freezing as long as they can keep a portion of the water fluid water is kept fluid by high salts (eg. making frozen yogurt or salt softening day off keeps water fluid underneath frigid temperatures) eg. there are a couple of harsh pools in Anarctica where water stays liquid at – 5º F (- 20.6º C )
Marine creatures for the most part can’t endure freshwaters and freshwater creatures by and large can’t endure sea water the saltiness of the untamed sea is an extremely steady 3% spineless creatures that live in the sea ordinarily generally approve of saltiness varieties since their bodies are a similar saltiness as the sea water arine vertebrates (for the most part fish) have cells that are marginally less pungent than seawater.
General Kinds of Ecosystems
All the world’s ecosystems can be grouped into just a two broad categories that share many similar characteristics that life in them must adapt to:
A. Aquatic Ecosystems (~73% earth’s surface)
B. Terrestrial Ecosystems (27% earth’s surface)
A. Aquatic Ecosystems
Water basedmost stable overall (most of ocean is 2º C) buoyancy of water reduces need for support less oxygen in water than in airlarger animals need more efficient extraction eg. gillsheavy dependence on chemical senses and ability to detect vibrations in water is an ideal medium for reproduction spawning motile larvae for dispersal doesn’t require internal fertilization
Two different kinds of aquatic ecosystems:
1. Marine
2. Freshwater
Marine Ecosystems
Freshwater Eco systems
Streams, rivers, lakes, ponds(<2% earth’s surface = less than the area of Europe)more variable in temperature, amount of light, nutrients, etc than marine very few salts in water FW systems are disproportionately rich in species and disproportionately imperiled FW ecosystems encompass <2% of earth’s surface they contain 12% of all animal species including 41% of all fish species but a much greater proportion of fw species are now endangered, threatened or at risk eg. 20-36% of all fw fish species eg. 67% fw clams eg. 64% crayfish species eg. 35% amphibians compare to terrestrial:eg. 17% of mammals; 11% of birds are at risk
B.Terrestrial Ecosystems
Community Interactions
In addition to interactions between the living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem, there are also numerous interactions between the living organisms themselves plants vs herbivores some animals have very specfic food needs eg. Panda eat only bamboo
Predators vs Prey
Symbiosis
ALL living beings including all creatures structure symbioses with different creatures and different lifeforms
Sorts of Symbioses
a. mutualism
b. commensalism
c. parasitism
a. Mutualism
The two life forms profit by the relationship eg. harmonious green growth in corals and wipes eg. protozoa in gut of termite eg. some gut microbes shield us from malady and microorganisms
b. Commensalism
One living being benefits, the other neither advantages nor is hurt (nonpartisan impact) eg. follicle bugs.
c. Parasitism
most common form of symbiosis eg. 20-50% of all animal species are paras