Compounds are proteins having tremendous synergist power, they incredibly improve the rate At which explicit synthetic responses occur.
Enzymatic Responses are Consistently Reversible.
Practically all catalysts are globular proteins comprising both of a solitary polypeptide or at least two polypeptides held together by non-covalent bonds. Catalysts follow up on different particles (substrate) and subsequently catalyze compound responses.
Accordingly, a compound is a natural impetus that is equipped for quickening a particular synthetic response by bringing down the necessary initiation vitality, yet unaltered itself all the while.
The reactants of enzymatic responses are classified “substrate”.
Definition
Haldane characterizes a chemical as a solvent, colloidal, natural impetus which is created by creatures. Noteworthy chronicled realities of chemicals
1. KIRCHHOF (1815): – First demonstrated the event of compounds in living frameworks.
2. LOUIS PAST EUR (1860): – Discovered that yeast cells can achieve the aging of groceries.
3. KUHNE (1878): – First gave the expression “Catalyst”.
4. BUCHNER (1897): – First arranged an unadulterated concentrate of “zymase” catalyst from yeast.
5. NOBEL LAUREATE SUMNER (1926): – First arranged unadulterated precious stones of “urease” catalysts from jack beans.
6. NORTHROP(1930): – Prepared unadulterated gems of the chemicals pepsin and trypsin separately from gastric juice and pancreatic juice
7. Lock and Key or Template theory was given by EMIL FISHER (1894) and adjusted by KOSHLAND (1971).
Structure
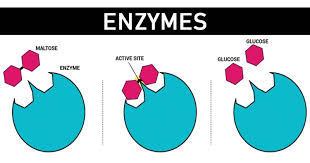
Compounds are globular protein particles that have three-dimensional shape with at any rate one surface district having a territory with a cleft or pocket.
The cleft possesses just a little segment of the catalyst’s surface and is known as its ACTIVE SITE . Their shape regularly give them at least one dynamic destinations (spaces) which tie fleeting riley and generally non-covalently with viable substrate atoms to frame at least one Enzyme – substrate (ES) buildings, catalysis happening just during the short presence of the complex.
Dynamic site is so formed so a substrate atom or a few particles fit into it in a quite certain manner and is held set up by frail compound powers, for example, hydrogen securities. Official of the substrate to the compound causes an adjustment in a chemical’s shape. This wonder of progress in a catalyst’s shape following authoritative of substrate is called ‘prompted fit’. This actuated fit hypothesis is upheld by X-beam crystallographic proof.
Proteins never really accelerate the rates at which the balance places of reversible responses are achieved.
Synthetic Nature of Chemicals
RNA Particle
It is presently referred to that RNA particles can go about as impetuses of responses, now and then including themselves as substrate. At the point when they include non-self RNA atoms as substrate, as some do, they can be viewed as proteins in the full sense.
For example, Ribozyme is chemically dynamic RNA particle. Their revelation in 1981 has enlarged the augmentation of the term ‘catalyst’ past proteins. A few ribozymes are self-joining introns, causing theory as intermediates in the advancement of organic frameworks from prebiotic ones.
Characterization and Terminology of Compounds
The main compound known was diastase.
Beforehand it was proposed that catalysts be named by including – ‘ase’ to root, characteristic of the idea of the substrate of chemical. Despite the fact that compounds are presently no longer named in such a straightforward way.
Presently compounds are normally grouped and named by the response the catalyze. A global code for proteins perceives six significant classifications of compound capacity, as follows:
1.Oxidoreductases
2.Transferases
Transferases catalyze the exchange of a gathering of iotas starting with one substrate then onto the next, for example, transminases move amino gatherings. A significant subclass of this gathering are the kinases , which catalyze the phosphorylation of their substrate by moving a phosphate gathering, for the most part from ATP, accordingly actuating the metabolically inactive compound for additional changes.
3.Hydrolases
Hydrolases catalyze hydrolysis responses. Catalyze the hydrolysis of proteins (protienases,peptidases), nucleic acids (nucleases), starch (amylases), fats (lipases), phosphate esters (phosphatases).
Numerous hydrolases are discharged by stomach, pancreas, digestive tract and are answerable for the processing of nourishments. For instance—Cholinesterase, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of acetylcholine, assumes a significant part in the transmission of apprehensive motivations. Hydrolases by and large catalyze expansion or evacuation of water particle.
4.Lyases
5.Isomerases
Any compound changing over an atom to one of its isomers, usually an auxiliary isomer, is called isomerase chemical. Isomerases catalyze the interconvert particle of isomeric mixes.
For instance—Triose phosphate isomerase catalyzes D-Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate into dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
6.Ligases( Synthetases)
Ligases perform buildup responses including ATP cleavage. Ligases or synthetases are compounds that catalyze endergonic combination, combined with the exergonic hydrolysis of ATP. They permit the synthetic vitality put away in ATP.
Elements affecting protein movement. Any condition that influences the three-dimensional state of a protein will impact its movement.
1. Grouping of A Substrate
The pace of Enzyme activity doesn’t increment past certain expansion in substrate fixation. Michaelis At any one moment, the extent of catalyst particles bound to substrate will rely on the substrate focus.
As this is expanded, the underlying speed of the response (v0) on expansion of chemical increments upto a greatest worth, Vmax at which substrate level the compound is supposed to be immersed (all dynamic destinations maximally involved) and no further expansion of substrate will build V0. The estimation of substrate focus at which V0=1/2Vmax is known as the MICHAELIS CONSTANT (Km) for the protein substrate response. Low Km shows high fondness of the catalyst for the substrate.
2. Convergence of an Enzyme
The speed of an enzymatic response is corresponding to catalyst fixation.
3. Impact of Temperature
The state of a protein is dictated by its hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonds are effortlessly Disrupted by temperature changes. For instance, higher warm blooded animals have compounds That capacity best inside a generally thin temperature rang somewhere in the range of 350c and 400c. Underneath 350c,the securities that decide protein shape are not adaptable enough to allow the Shape change important for substrate to fit into a receptive site.
Over 400 c,the bonds are too frail to even consider holding the protein in appropriate position and keep up its Shape. At the point when appropriate shape is lost, the catalyst is annihilated; this loss of shape is called ‘denaturation’.
4. Impact of pH
Most proteins likewise have a pH ideal, generally between 6to 8. For instance, when the pH is excessively low, the H+ particles consolidate with the R-gatherings of the chemical’s amino acids, decreasing their capacity to tie with substrate.
Corrosive situations can likewise denature proteins. That is the reason a few chemicals work at a low pH. For instance, pepsin is the chemical found in the stomach of well evolved creatures and has an ideal pH of around 2. Alternately trypsin is dynamic in the more essential medium (pH 9) and found in small digestive system. By and large the pH ideal of a chemical mirrors the pH of the body liquid wherein the protein is found.
5. Cofactors and Coenzymes
Cofactors are metal particles.These particles regularly give a required change inside a functioning site.
Numerous proteins utilize metal particles to change a non-working dynamic site to a working one. In these chemicals, the connection of a cofactor causes a shape change in the protein that permits it to consolidate with its substrate.
The cofactors of other chemical partake in brief connections between the catalyst and its substrate when the protein substrate (ES) complex is shaped.
Coenzymes are non-protein, natural particles that take an interest in chemical synergist responses, regularly by moving electrons as hydrogen molecules, starting with one compound then onto the next. Numerous nutrients work as coenzymes or are said to make coenzymes (e.g., Niacin and Riboflavin)
Allosteric Enzymes
Allosteric chemicals have, notwithstanding a functioning site, another sound system explicit site to which an effectors or modulator atom can tie. At the point when it does, the state of the dynamic is modified so it can or can’t tie substrate (allosteric incitement or restraint separately). Along these lines the compound can be essential for a fine control circuit, requiring the presence or nonattendance of a substrate notwithstanding substrate introduced before catalyst movement continues. Some allosteric catalysts react to at least two such modulators, allowing still better authority over planning of compounds movement.
8. Protein Inhibition.
Protein hindrance is the avoidance of a catalyst cycle because of the communication of some substrate with a compound in order to diminish the pace of the enzymatic responses
Mechanical Uses of Chemicals
1. Proteins in medication
The protein thrombin is utilized to advance mending of wounds.The protein lysozyme wrecks cell mass of microscopic organisms.
Proteins may in the end we used to control chemical insufficiencies and irregularities coming about because of illnesses.
2. Some of the proteins are utilized as cleansers eg. Amylase
3. Some catalysts are utilized ventures for doing concoction responses
4. Some catalysts are utilized in food creation and Chemical amalgamation of different mechanical items.
5. Certain proteins are utilized in measure of different substrates and items