There are following model which set forward time to time to clarify structure of plasma layer:
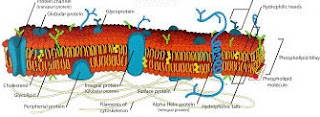
Danielli and Davson (1935) proposed a “Trilamellar model”. As indicated by this, the plasma film is framed of a bimolecular layer of phospholipids (35 Å thick) sandwiched between two layers of proteins (every 20 Å thick).
Along these lines, the all out thickness of plasma film, according to their model, ought to be 20 Å + 35 Å + 20 Å = 75 Å (i.e., around 75 Å).
The model was proposed even before the plasma film was seen under the electron magnifying instrument.
J.D. Robertson (1959) proposed a “unit film idea”. As per this, every single organic film had a similar essential structure:
(a) These are around 75 Å thick.
(b) These have an attributes trilaminar appearance when seen with electron magnifying lens.
(c) The three layers are an aftereffect of indistinguishable course of action of proteins and lipids from proposed by Danielli and Davson.
Vocalist and Nicolson (1972) set forward the “liquid mosaic model” of layer structure. It is the most recent and most broadly acknowledged model. As per this model, the cell film comprises of an exceptionally thick liquid grid of two layers of phospholipids atoms.
These fill in as a generally impermeable hindrance to the section of most water solvent particles. Protein atoms on their buildings happen in the film, however not in ceaseless layer; rather, these happen as discrete particles unevenly orchestrated in a mosaic example.
A portion of these (fringe or outward proteins) are inexactly bound at the polar surfaces of lipid layers. Others (called necessary or inherent proteins), enter profoundly into the lipid layer.
A portion of the vital proteins enter through the phospholipids layers and venture on both the surfaces. These are called Trans films or passage proteins. Transport across Membranes
A. Development of Small Molecules across Membranes can include basic dissemination or protein-interceded transport:
Latent Diffusion.
Lipophilic solutes cross the film unreservedly by dissolving in the lipid bilayer. This is aloof dispersion. Models: ethanol (liquor, contains both polar and non-polar districts); likewise unsaturated fats, glycerol, steroids, and so forth. Additionally nonpolar gases like O=O (O2).
Specific vehicle by protein transporters – permeases.
Polar or ionic little solutes might be shipped across films if explicit protein transporters are in the layer. Models: sugars, amino acids, particles. Numerous substances can’t cross the layer. Models: enormous atoms, for example, proteins, nucleic acids. Additionally little polar atoms or particles for which there is no protein transporter.
B. Some protein transporters require vitality; others don’t. There are 2 potential circumstances:
Encouraged dissemination Membrane has explicit protein bearer, will tie to atom and bring it across cell film.
No vitality required.
No particular bearing.
On the off chance that particle is more focused outside than inside cell, net development will be out of cell. Models incorporate .
Glucose transporters-5 diverse GLUT proteins and 2 sorts that cotransport Na and glucose (these are utilized for optional dynamic vehicle)
Water channels-8 distinct kinds of aquaporins.
Dynamic vehicle Membrane has explicit protein bearer, additionally a prerequisite for vitality (ATP or other type of vitality). Will move solute against a fixation angle, so can think material regardless of whether dissemination would support inverse course of stream.
Model: Na+-K+ ATPase in nerve cells. Siphons Na+ to outside, K+ in, keeps up electrical potential against dispersion. At the point when nerve cell “fires” the flitting doors open to allow dissemination to happen. At that point siphons are betrayed to reestablish potential.
Dynamic vehicle can include ATP siphons, symport, or antiport.
C. Development of Large Molecules Large atoms (proteins, nucleic acids, polypeptides bigger than a couple of amino acids, polysaccharides bigger than a couple of sugars) are not conveyed by transport proteins.
There are components for moving bigger particles, however they don’t go into cytoplasm.
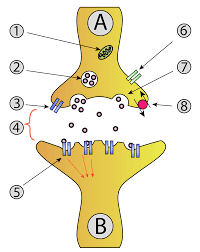
Exocytosis.
Membrane vesicle wires with cell layer, discharges encased material to extracellular space. Ex: arrival of stomach related catalysts from pancreatic cells; bodily fluid, milk, hormones, and so forth.
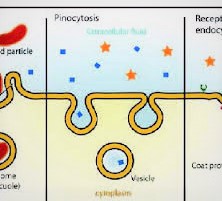
Endocytosis
Cell film invaginates, squeezes in, and makes vesicle encasing substance. Three normal circumstances:
Phagocytosis
Regularly chips away at trash, microbes, and other particulate issue. Substance of the “phagosome” are normally intertwined with lysosome to make “phagolysosome”, where material is separated. This is particularly normal in white platelets, for example, macrophages and different leukocytes.
Like Phagocytosis, however ingests liquid instead of particulate issue called “Cell drinking”. Ex. cells lining blood vessels take liquid from blood (however not red cells), move liquid over their cytoplasm, discharge into extracellular space encompassing cells outside the narrow.
Bearer interceded endocytosis (CME)/receptor-intervened endocytosis.
It is an exceptionally particular framework. Certain significant atoms or particles are not brought into cell by transport forms, however by CME. The body utilizes hormones to control film transport right now
Iron is brought through blood firmly bound to transferrin protein bearer.
To get iron into cells, cell film contains extraordinary receptor proteins that quandary transferrin, move towards exceptional districts of layer under which lie clathrin proteins.
Endocytosis happens inside clathrin “confine”, moves inside cell. Confine in the long run reuses back to cell surface, returning transferrin proteins to cell outside. In any case, iron is discharged inside cell, exits from vesicles, and gets bound to ferritin
http://feeds.feedburner.com/ecarepk
Post Views:
52