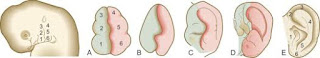
External ear –
The substantial part outside the head is known as the pinna. It is included flexible tendon and skin. It is followed by the external hear-capable meatus. This part is fixed with hairs and ceruminous organs. These organs produce cerumen or earwax. The hair and wax shield new articles from showing up at the ear drum. The ear drum or tympanic film is an oval, three layered structure. It separates outside and focus ears.
Focus ear –
Internal ear –
This locale has entries and chambers inside the brief bone called the hard labyrinth. The hard labyrinth contains three areas called the cochlea, vestibule and sickle streams.
The oval window found in the middle and internal ears talks with the vestibule of the internal ear. The organs of the inner ear see the sound.
Genuine ear is a touchy
Organ arranged in the brief region of the skull. It is called membranous labyrinth, which created in unrefined vertebrates for help of equality and position. Hearing limit of this organ progressed unprecedented for anurans when they started living in terrestrial condition, where sound waves adventure out snappier and to longer detachments.
A customary membranous labyrinth involves three channels and three sacs. The three channels are associated at right edge to each other and to the sacs in premier, back and even positions. The three sacs which are furthermore all around called vestibule are:
Utriculus, sacculus and lagena, each and every one of which has a decline inside with a material organ considered macula that recognizes the circumstance of the body as per gravity, or static sense. Each channel shut in an ampulla that in like manner passes on a sense organ called crista,
Which is liable for area of the advancement of head toward any way, or engine sense. Both these resources together keep up the balance and position of the animal during its development. Endolymph fills the membranous labyrinth and is released and drained in meninges. Perlilymph incorporates the membranous labyrinth for protection.
The structure of crista looks like any neuromast organ of fishes. It includes unmistakable cells with hairs on the top and nerve strands joined underneath and many supporting cells that continue and guarantee the material cells. Hairs of substantial cells are introduced in a thick mass called cupula terminalis in which a couple of valuable stones are embedded basically over the hair tips. As the animal moves these diamonds similarly move and contact the hairs of unmistakable cells, which produce nerve inspirations that take the dynamic sense to the cerebrum. This is called dynamic equalization kept up by the sickle streams.
Macula is the material organ of sacs. Its substantial cells moreover have hairs on the top and nerve at the base anyway the cells are of two sorts, specifically, round and empty cells and container framed cells which bear stereocilia and kinocilia introduced in a coagulated mass. A paper slim otolith made of calcium carbonate and proteins skims over the cilia and its position can be furious about the animal bowing or slanting toward any way relating to gravity, upsetting the cilia at the same time and creating a nerve drive that lights up the psyche with respect to static sense.
CYCLOSTOMES
Cyclostomes have declined membranous labyrinth due to their parasitic technique forever. Petromyzon has only two half hover channels, to be explicit the principal and back and only two sacs, utriculus and sacculus, lagena being missing. As they have no coordinated edges, lampreys and hagfishes don’t seem to have three dimensional sentiment of things. In hagfishes, the premier and back channels in like manner join to make a ring like structure. Sacculus and utriculus furthermore merge to outline a singular sac.
FISHES
Fish membranous labyrinth is generally made with three channels and three sacs, and crista and macula especially encircled. In elasmobranchs a recessus utriculus is attached on the lower side of utriculus. Macula of utriculus is eventually called principles neglecta in fishes.
AMPHIBIA
REPTILES and BIRDS
In reptiles and winged creatures lagena drags out and basilar papilla disclosed to shape the organ of corti, which is generously more delicate to see sound vibrations. Columella bone is called stapes, which is moreover delayed by the choice of an extrastapaedial tendon.
For better security, tympanic layer sinks into the transitory bone, conveying a hear-capable channel, through which sound vibrations make an outing from outside to the tympanic film. In crocodiles lagena is wound like cochlea of warm blooded creatures. In reptiles both Eustachian tubes consolidate to open into pharynx by a lone opening.
In snakes there are no external and focus ear miseries and subsequently strong vibrations head out through ground to the lower jaw and starting there to quadrate uncertain issue, which passes on them to lagena of inward ear for impression of hearing. Thusly, snakes can’t hear sounds experiencing air.
Fowls have essentially relative segment of hearing as do the reptiles, on the other hand, really ear is considerably more fragile in winged creatures due to expansion of lagena.
Warm blooded animals
Warm blooded animals have the best advanced hearing power among all vertebrates. Lagena stretches out to shape a spirally circled cochlea. In focus ear gap, as opposed to one bone, warm blooded animals have three ear ossicles, specifically, incus ( an auxiliary of pterygoquadrate), malleus (a subordinate of articular or meckel’s tendon) and stapes (got from hyomandibular), which convey sound vibrations from tympanic layer to the fenestra ovalis that prompts scala vestibuli of cochlea. Warm blooded animals moreover have various sizes of ear pinna to accumulate
Sound waves and direct them to the hear-capable channel.
Cochlea is a specific and especially tricky sense organ of hearing. Its cross region reveals three long chambers, specifically, scala vestibuli, scala media and scala tympani, the middle chamber is stacked up with endolymph while the other two are stacked up with perilymph.
The organ of corti is associated with the basilar film and passes on material hair cells and supporting cells and the cochlear nerve at the base. A tectorial layer skims in scala media and contacts the hairs of material cells when it vibrates by the sound vibrations, achieving the age of a nerve inspiration that developments through the cochlear nerve to the cerebrum.
Base of cochlea is more delicate to high repeat vibrations while the apical part can distinguish very weak vibrations. Sound waves from stapes enter scala vestibuli through fenestra ovalis or oval window, by then travel to the entire length of cochlea and return back by methods for scala tympani and flight to the middle ear pit through fenestra rotunda or round window.
Human ear is prepared for hearing sound waves reaching out from 20 to 20,000 hertz yet different very much developed animals have capacity to hear traces of different frequencies. For instance, whales, dolphins and porpoises can hear ultrasonic traces of up to 150,000 hertz and elephants can in like manner hear infrasonic traces of 10-14 hertz.