A T cell, or T lymphocyte, is a sort of lymphocyte (a subtype of white platelet) that assumes a focal function in cell-interceded resistance. Immune system microorganisms can be recognized from different lymphocytes, for example, B cells and common executioner cells, by the presence of a T-cell receptor on the cell surface. They are called T cells since they develop in the thymus from thymocytes (albeit some additionally develop in the tonsils.
The few subsets of T cells each have a particular capacity. Most of human T cells revamp their alpha and beta chains on the cell receptor and are named alpha beta T cells (αβ T cells) and are important for the versatile safe framework. Specific gamma delta T cells, (a little minority of T cells in the human body, more incessant in ruminants), have invariant T-cell receptors with restricted assorted variety, that can successfully introduce antigens to other T cells and are viewed as a major aspect of the inborn safe framework.
Types
Effector
The classification of effector T cell is an expansive one that incorporates different T cell types that effectively react to an improvement, for example, co-incitement. This incorporates partner, executioner, administrative, and conceivably other T cell types.
Partner
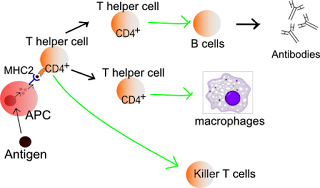
T partner cells (TH cells) help other white platelets in immunologic cycles, including development of B cells into plasma cells and memory B cells, and actuation of cytotoxic T cells and macrophages. These cells are otherwise called CD + T cells since they express the CD glycoprotein on their surfaces.
Partner T cells become actuated when they are given peptide antigens by MHC class II atoms, which are communicated on the outside of antigen-introducing cells (APCs). When actuated, they isolate quickly and emit little proteins considered cytokines that control or aid the dynamic resistant reaction.
These cells can separate into one of a few subtypes, including TH , TH , TH , TH , TH , or TFH, which emit various cytokines to encourage various sorts of invulnerable reactions. Motioning from the APC coordinates T cells into specific subtypes.
Cytotoxic (executioner)
The executioner cell at that point utilizes uncommon synthetic substances housed in vesicles (red) to convey the murdering blow. This occasion has along these lines been nicknamed “the kiss of death”. After the objective cell is murdered, the executioner T cells proceed onward to locate the following casualty.
Cytotoxic T cells (TC cells, CTLs, T-executioner cells, executioner T cells) pulverize infection contaminated cells and tumor cells, and are likewise embroiled in relocate dismissal. These cells are otherwise called CD + T cells since they express the CD glycoprotein at their surfaces. These cells perceive their objectives by authoritative to antigen related with MHC class I atoms, which are available on the outside of every single nucleated cell.
Through IL-, adenosine, and different atoms discharged by administrative T cells, the CD + cells can be inactivated to an anergic state, which forestalls immune system maladies.
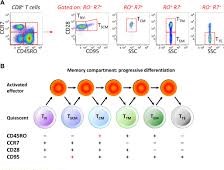
Memory
Antigen-guileless T cells grow and separate into memory and effector T cells after they experience their related antigen inside the setting of a MHC atom on the outside of an expert antigen introducing cell (for example a dendritic cell).
Suitable co-incitement must be available at the hour of antigen experience for this cycle to happen. Generally, memory T cells were thought to have a place with either the effector or focal memory subtypes, each with their own distinctive arrangement of cell surface markers (see below).[Subsequently, various new populaces of memory T cells were found including tissue-inhabitant memory T (Trm) cells, stem memory TSCM cells, and virtual memory T cells.
The single bringing together subject for all memory T cell subtypes is that they are seemingly perpetual and can rapidly grow to huge quantities of effector T cells upon re-presentation to their related antigen. By this component they give the invulnerable framework “memory” against recently experienced microbes. Memory T cells might be either CD + or CD + and generally express CD RO.
Memory T cell subtypes
1. Central memory T cells (TCM cells) express CD RO, C-C chemokine receptor type (CCR ), and L-selectin (CD L). Focal memory T cells additionally have middle of the road to high articulation of CD . This memory subpopulation is ordinarily found in the lymph hubs and in the fringe dissemination. (Note-CD articulation is typically used to recognize murine credulous from memory T cells).
2. Effector memory T cells (TEM cells and TEMRA cells) express CD RO however need articulation of CCR and L-selectin. They likewise have middle of the road to high articulation of CD . These memory T cells need lymph hub homing receptors and are consequently found in the fringe course and tissues.TEMRA represents terminally separated effector memory cells re-communicating CD RA, which is a marker generally found on credulous T cells.
3. Tissue inhabitant memory T cells (TRM) possess tissues (skin, lung, and so forth..) without recycling. One cell surface marker that has been related with TRM is the integrin αeβ
4. Virtual memory T cells vary from the other memory subsets in that they don’t start following a solid clonal extension occasion. Accordingly, in spite of the fact that this populace overall is bountiful inside the fringe dissemination, individual virtual memory T cell clones live at moderately low frequencies.
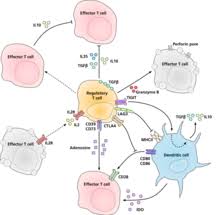
Administrative (silencer)
Administrative T cells (silencer T cells) are pivotal for the upkeep of immunological resilience. Their significant job is to close down T cell-interceded invulnerability around the finish of an insusceptible response and to stifle autoreactive T cells that got away from the cycle of negative choice in the thymus. Silencer T cells alongside Helper T cells can by and large be called Regulatory T cells due to their administrative functions.
Two significant classes of CD + Treg cells have been portrayed — FOXP + Treg cells and FOXP − Treg cells.
Administrative T cells can grow either during typical advancement in the thymus, and are then known as thymic Treg cells, or can be prompted incidentally and are called incidentally inferred Treg cells.
These two subsets were recently called “normally happening”, and “versatile” or “actuated”, respectively.Both subsets require the statement of the record factor FOXP which can be utilized to distinguish the phones. Changes of the FOXP quality can forestall administrative T cell improvement, causing the deadly immune system sickness IPEX.
A few different sorts of T cell have suppressive movement, however don’t communicate FOXP . These incorporate Tr cells and Th cells, which are thought to begin during a safe reaction and act by delivering suppressive particles. Tr cells are related with IL-, and Th cells are related with TGF-beta. As of late, Treg cells have been added to this rundown