Core Technique in Biotechnology: PCR-gel Electrophoresis
this is the selective amplification method for the particular segment of the DNA in vitro. this is the basic method that is performed in all molecular labs.
Basic feature:
- very robust technique/method:
The template of the DNA is not highly purified in this method. only a small boiled bacterial colony or a small piece of the leaf of any plant is sufficient to perform this technique.
- highly sensitive and precise method:
If the reaction is performed carefully than even a small piece of DNA can produce a highly significant visible band.
- but contaminated specimen like reagents or pipette can give false report.
Discovery:
- He was awarded with noble prize in 1993 in chemistry.
- The basic principle of replication using a piece of DNA by using two primers this method was already described by Gobind Khorana in 1971.
- Because of primer synthesis and polymerase issue the progress in this method stay limited.
- It was Mullis who properly explain all this procedure.
- He was awarded with noble prize in 1993 in chemistry.
- The basic principle of replication using a piece of DNA by using two primers this method was already described by Gobind Khorana in 1971.
- Because of primer synthesis and polymerase issue the progress in this method stay limited.
- It was Mullis who properly explain all this procedure.
What is in this reaction:
- Template of DNA.
- PCR buffer is also required.
- nucleotides(dNTPs).
- the primers.
- DNA polymerase enzyme.
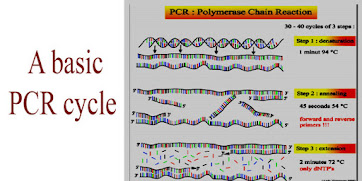
this reaction is performed in the automatic thermal cycler that was introduced in the 1986. but before it this PCR reaction was performed in three different water baths for three steps like:
- denaturation
- annealing
- extension
DNA polymerase:
- DNA is ever synthesized in the direction of 5′ to 3′ direction and use only in the extension step.
- Commonly used polymerase in this process is Taq polymerase that is obtained from thermus aquaticus.
- It is the heat stable polymerase.
- The ideal temperature for it is 72 C.
- This process include incorporation of 150 nucleotides per second by using the template of DNA.
Amplifiable size of the target:
- Product of PCR is about 100 to 1500bp in the size.
- It also depends on the amplification capacity of the the enzyme that is used in this process.
Primer:
- Primers are about of the size of 20bp and are specific for target.
- primer should make complementary base pairing with each other or should make secondary structure.
- And the annealing temperature of the both primer should be must similar.
Application of PCR:
- This method is used for the amplification of small segment of the DNA that is used for the purpose of sequencing, manipulation of genes or cloning of the gene or the region of the gene.
- This method is useful in the diagnosis of different disease including genetic disorders.
- This process is also used in the forensic lab and to resolve legal matters of crime .
- This process is used for the purpose of genes mapping and for the study of gene diversity.
- Used for the selection of molecular marker and for QTL mapping.
- It is used to validate the level of transcription
Agarose-gel electrophoresis
Application of agarose gel electrophoresis:
- It is used for the analysis of the product of PCR reaction and to analyze restricted fragments of DNA.
- It used for the estimation of the size of the molecule of RNA or DNA.
- It also used for the calculation of the concentration of the molecule of RNA or DNA.
- It is also used for the separation of nucleic acid molecule for the purpose of southern or northern hybridization.
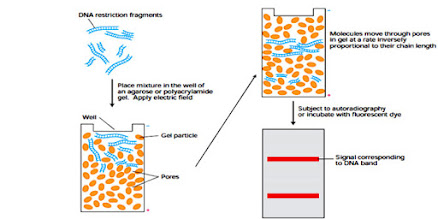
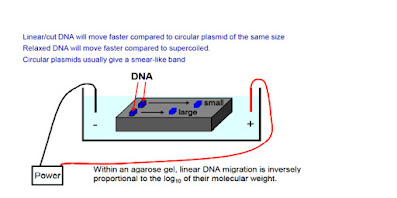
- DNA having negative charge when place on the agarose gel under the influence of electric charger it moves towards the positive electrode.
- The use of agarose gel in this technique is to slow down the movement of DNA or RNA molecule in order to make sure that they separated by size.
- When the voltage is high than greater force is exerted onto the DNA molecule that’s why fragments move faster in the agarose gel’s matrix.
Sample preparation and loading:
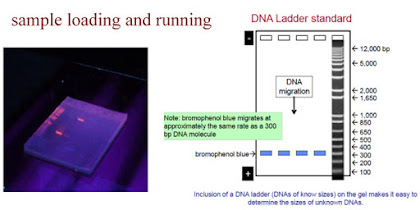
- First of all we have to mix up the sample with loading buffer which contain bromophenol blue and glycerol.
- Glycerol increase the density of the sample and keep the sample sink.
- The function of bromophenol blue is to keep the track of the sample moving through the gel.
- The commonly used buffer are :
- TAE( which is tri-acetate-EDTA)
- TBE(tri-borate-EDTA)
- Buffer in addition to maintain pH provides ions to support conductivity.
- To keep the exact voltage while sample is running through the gel is important to get good resolution.
- More high voltage can melt the gel too.
- When the voltage increase the large fragments starts moving faster as compare to the shorter one.
- For visualization of DNA or RNA the gel are stained with ethidium bromide which fluorescence under UV light.