What are the requirements for the growth and development in plants:
- cell division plays its role in the reproduction and growth of the plant cell its mean in the cell repairing and renewal cell division involves.
- cell cycle is the mechanism in which cells reproduce themselves and the genetic material which is DNA is also reproduced.
- the four phases of the cell cycle are G1, S, G2 and M-stages.
- the cell cycle consist of the :
- Interphase; which further consist of the G1 , S and G2 stages . this is the important step in cell cycle as it is necessary for the duplication of the DAN and also for the start up of the process of mitosis.
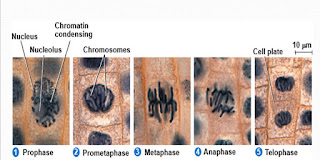
- while mitosis consist of ; prophase, pro-metaphase, metaphase and anaphase and telophase. the function of the mitosis is to divide the original parent cell into two daughter cell with equal amount of genetic makeup in each daughter cell.
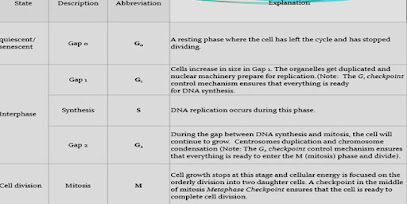
Different Phases of the cell cycle:
- Interphase ( involves growth and development of the cell and duplication of the genetic material DNA ( chromosome) actually it is preparation of the cell to undergo into the division phase.
- mitotic phase which is commonly called M-phase it involves mitosis and cytokinesis .
Sub-phases of the interphase( which is about 90 percent of the cell cycle):
- G1-stage which is known to be first gape.
- S stage which is known as synthesis phase.
- G2- phase which is second gap.
- duplication of chromosome take place only in the S phase although cell keep on growing in all these three phases.
Activities during the phases of the cell cycle:
- each phase of the cell cycle has a specific and unique type of biochemical and cellular activities.
- there is the key regulatory point in the starting G1-phase of the cell cycle where cell decided to commit to the initiation of the DNA synthesis. this point can be said as Start point.
- When a cell cross this start point this process becomes irreversible. so now the cell is committed to the DNA synthesis and than following the process of mitosis and cytokinesis.
- when the cell once completed the mitosis phases cell can again start the complete cell cycle. or it can leave the cell cycle and start the process of differentiation.
- this kind of choice is ever made at the critical regulatory point at the g1 stage , this is before cell start the replication of the DNA.
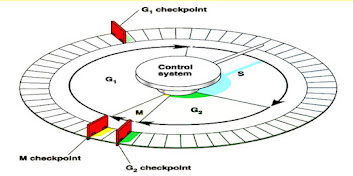
Cell cycle control:
- The critical control point in the cell which is also called checkpoint. this is the exact point where stop signal and the go signal can regulates the cell cycle.
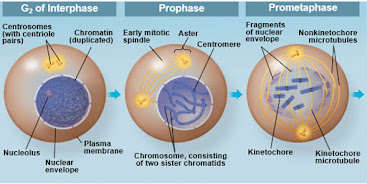
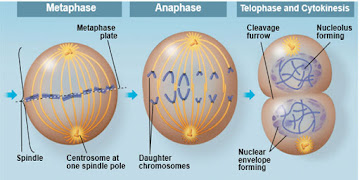
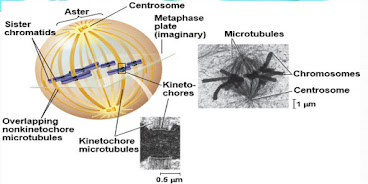
Mitosis in animal cell:
The mitotic spindles at metaphase:
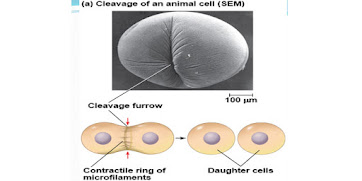
Cytokinesis:
- in animal cell cleavage furrow formation lead to the process called cleavages which is the process of cytokinesis in animal cell.
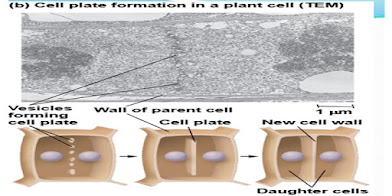
- in case of animal cell cell plate form which leads to cytokinesis.
Mitosis in plant cell:
Cytokinesis in plant cell:
Explanation of activities in different phases of cell cycle:
Difference between the animal and plant’s cell cycle:
- some of the cells of mammals when they have stopped dividing it can happened that it can reenter into the cell cycle by the action of variety of hormone and different growth factor.
- when mammalian cell do so they can do so can enter to the cell cycle at the critical point at the start of the G1 phase.
- as compare to animals cells, plant cells can leave the cell cycle either before or after the replication of DNA. this happened during G1 or G2 phase. because of this step where most of the animals cells are diploid having two sets of chromosome most of the plant cells are tetraploids having four sets of chromosome and cells can be polyploids mean these having many sets of chromosomes, after going through the additional cycle of DNA replication this is without mitosis process.
Cell cycle control:
- cell have in-built stop signal that keep on stopping the cell cycle stop at the check point till signal came from the go signal .
- for functioning properly the check point signals must have to percept “report” from the crucial cellular processes:
- that either it have successfully done correctly and either cell cycle should proceeded .
- checkpoints also have register signals from outside the cell.
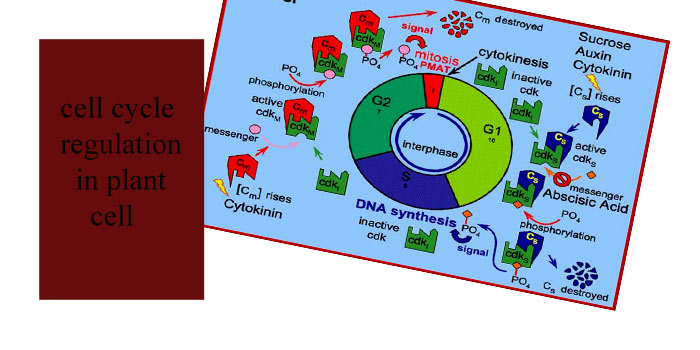
Cell cycle regulation in plant cell:
- the rate and timing of the cell cycle varies from organism to organism and even between it is different in different cells.
Cell cycle regulation at molecular level:
- experimental evidence give proof that cell cycle regulation is carried out by different chemical kind of signals that are present mostly in the cytoplasm.
- for this purpose most the experiment are conducted with cell culture.
- for this purpose most the animal and plant cells can be removed from the organism and can be cultured in the laboratory in the artificial medium.
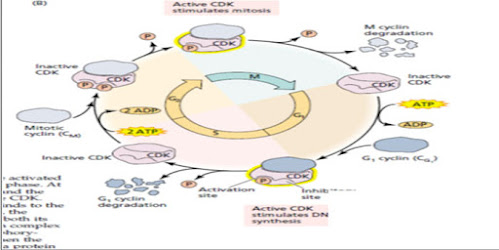
The regulation of cell cycle by the protein kinases:
- the basic key enzyme that has the ability to control over the transition among the different phases of the cell cycle and the permission for the entry of the non-dividing cell into the cell cycle is cyclin dependent kinases, or can be called as CDKs.
- protein kinases are those enzymes that involve in the function of phosphorylation of protein by using ATP.
- the regulated function of the CDKs is essential for the change of G1 stage into the S stage and the change of G2 stage into the M-stage and essential also for the entry of the non-dividing cell into the dividing cell cycle.
- it is observed from the experiments that the level of cyclin rise during the G2 phase and it will fall during the mitosis phases.
the activity of CDKs can be regulated by different ways but the most common ways are :
- the synthesis and destruction of cyclin.
- the process of phosphorylation o dephosphorylating of the basic and key amino acid residues present within the CDKs proteins.
- cyclin dependent kinases are inactive unless they are in association with the cyclin.
- they are synthesized and than similarly degraded at the specific point of the cell cycle by the usage of the ATP.
- the change of G1 phase into the S phase needs set of cyclin that is called G-1 cyclin that is different from the cyclin that are required in the change of g-2 phase into the m-phase where M-cyclin are required for the activation of CDKs.
- CDKs have two tyrosine phosphorylation sites : one site is responsible for the activation of the enzyme and the other site causes the inactivation o the enzyme .there are specific kinases which have the ability to perform both the stimulatory and inhibitory action of phosphorylation.
- similarly there specific protein phosphatases which can either add or remove phosphate group from the CDKs it can either stimulate or inhibit its activity it depends on the position of the phosphate group.
- the process of addition or removal of phosphate from CDKs is very important step in cell cycle regulation of cell cycle and its progress.
- there are also cyclin inhibitors which also plays important role in the regulation of the cell cycle in animal and plant cells in plant cells they are known as plant cell cyclin inhibitors .